The experiment aims at the digitalization of an injection moulding process for quick process set-up and production optimization.
MOTIVATION
Inymon,'s core business is the injection and decoration of small to medium-sized plastic parts. For every new part to put in production by INYMON, process set-up and optimization is a key phase to keep the company competitiveness in an extremely time and cost demanding market.
Today, this adjustment is performed based on experience and through trial and error loops. The use of simulation tools to design the injection process of thermoplastic parts is common practice in the plastics processing industry. Basically, these tools available in commercial packages such as Moldflow, Moldex3D etc. are used in the mould design stage, with the main objective of anticipating manufacturing problems and finding an “a priori” solution analysing alternatives of part and mould design, thereby reducing development costs and development time. However, the use of these tools for process set-up and parameter optimization is much less common and based on a trial-and-error approach.
When the mould is already built and the piece goes into production, it is no longer feasible to perform such simulations to make decisions about the adjustments to be made on the line in the event of any variation produced, due to the excessive time it would take to make them. This constitutes a significant loss of opportunity since the power provided by simulation tools reproducing the physics of processes stops being useful because of the impossibility of having results immediately, which is the necessary requirement in decision-making to control the process in the injection line.
"...reproducing the physics of processes stops being useful because of the impossibility of having results immediately, which is the necessary requirement in decision-making..."
Purpose of the Experiment
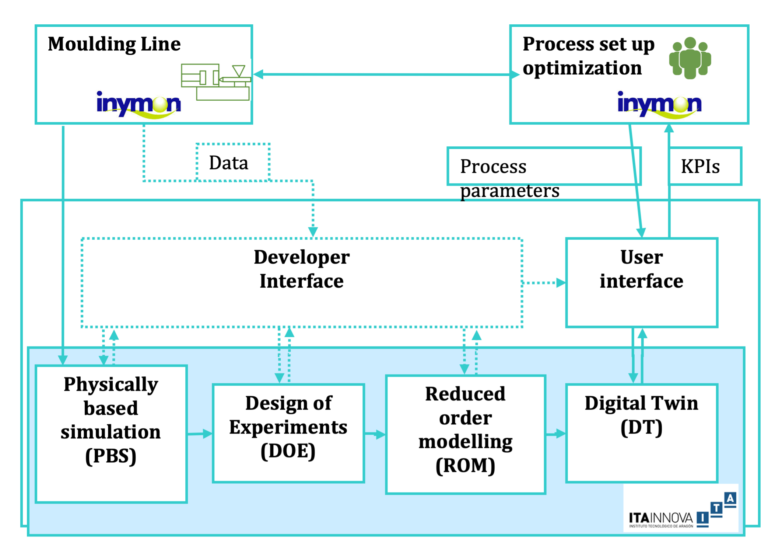
ITAINNOVA will extend CAELIATM Injection app used by Inymon already: a configurable service for reducing time-to-production in the set-up phase and for reducing cycle times during production.
To have available a tool/service that supports the injection moulding process optimization based on simulations accounting for the physics of the problem behind will be very useful for Inymon. This knowledge based tool will support the selection of proper process parameters that minimize the injection cycle time whilst keeping quality indicators of the selected part within tolerances. The resulting tool will be primarily used at the workshop, so it must be simple and user-friendly, requiring only a minimum of training and not necessarily having modelling experience to use it. To allow it, a graphical web-based user interface will be allocated in the DIGITBrain platform, where the process engineer will try different machine settings in a virtual environment. MONTIMAGE served as the technology partner and developed a SaaS that allows user to load ROM models and interface with available experimental data from the injection line.
.
Technical Impact
The main impact for the injection moulding industry is that the process setup is guided by the knowledge provided by the simulation tools, which account for the physics of the process. That is, the knowledge that the physics-based simulation tools provide extends from just being used in the mould design stage, to the process set-up and the part production stages.
This approach complements other commonly used approaches purely based on data captured in the injection line and applying Machine Learning techniques. The main contribution of the present approach is that it provides insight to the process engineer from the very beginning when the mould is set up and there is still no real data available in the monitoring system. In addition, it also provides a layer of interpretability of what happens inside the mould, complementing usually black-box approaches based on neuronal networks.
To achieve this point, the developer previously has to complete a sequence of activities. First to establish the proper knowledge-based simulation model that represents the injection process steps (filling-packing-cooling-part release) and which outputs are estimations of the part quality indicators. These simulations will be exploited through a simulation DOE that will allow exploring the processing window. Reduced-order techniques will allow encapsulating these results in simple models that run on the fly and that will constitute a Digital Twin of the process, being operable through the user interface. Based on data collected directly in the injection line, the developer can also update/correct the Digital Twin for achieving higher accuracy.
Expected Economic Impact
The main economic impact is that CAELIATM-Injection app will allow reducing the time/cost required for process set-up, reducing the number of trials as well as the material waste, energy consumed, machine and operator non-productive hours during this process.
Also, the opportunities of optimization using the tool are much higher than with the current practice, as the ROM provides a continuum output solution over the whole range of input parameter values.
Project Partners
INYMON
will define the injection process of reference for the experiment and will provide available collected data from online sensoring of the process.
ITAINNOVA
the Digital Innovation Hub in this experiment, will extend CAELIATM-Injection app: a configurable service for reducing time-to-production in the set-up phase and for reducing cycle times during production.
MONTIMAGE
will develop a reconfigurable user interface that can load ROM models and interface with available experimental data from the injection line.




